Ale
Ale is a type of beer brewed from malted barley using a top-fermenting brewers' yeast. This yeast ferments the beer quickly, giving it a sweet, full bodied and fruity taste. Most ales contain hops, which impart a bitter herbal flavour that helps to balance the sweetness of the malt and preserve the beer.
Varieties of Ale

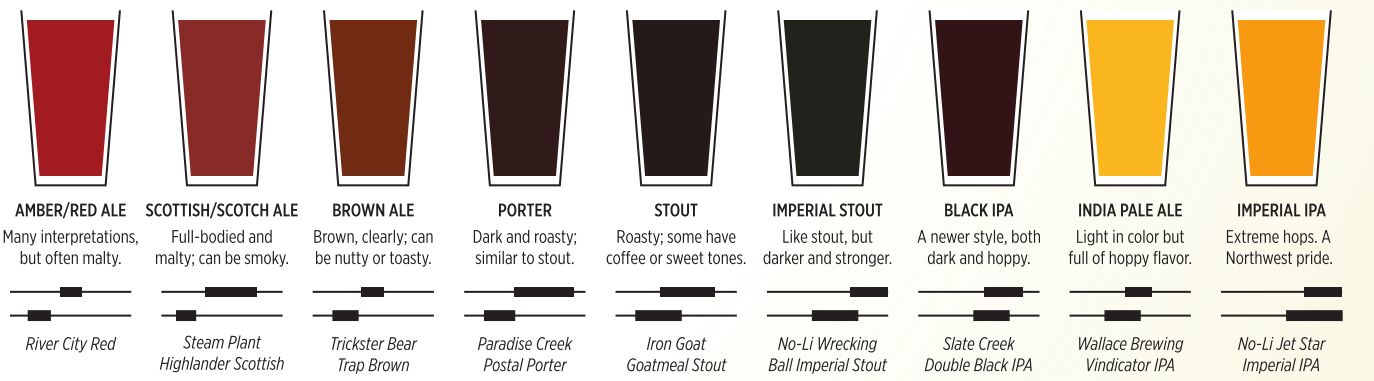
Brown ale
A darker barley malt is used to produce brown ales. They tend to be lightly hopped, and fairly mildly flavoured, often with a nutty taste. In the south of England they are dark brown, around 3-3.5% alcohol and quite sweet; in the north they are red-brown, 4.5-5% and drier. English brown ales first appeared in the early 1900s, with Manns Brown Ale and Newcastle Brown Ale as the best-known examples. The style became popular with homebrewers in North America in the early 1980s; Pete's Wicked Ale is an example, similar to the English original but substantially hoppier. Belgian oud bruin is a sour brown ale.
Pale ale
Pale ale was a term used for beers made from malt dried with coke. Coke had been first used for roasting malt in 1642, but it wasn't until around 1703 that the term pale ale was first used. By 1784 advertisements were appearing in the Calcutta Gazette for "light and excellent" pale ale. By 1830 onward the expressions bitter and pale ale were synonymous. Breweries would tend to designate beers as pale ale, though customers would commonly refer to the same beers as bitter. It is thought that customers used the term bitter to differentiate these pale ales from other less noticeably hopped beers such as porter and mild. By the mid to late 20th century, while brewers were still labeling bottled beers as pale ale, they had begun identifying cask beers as bitter, except those from Burton on Trent, which tend to be referred to as pale ales regardless of the method of dispatch.
Scotch ale
While the full range of ales is produced in Scotland, the term "Scotch Ale" is used internationally to denote a malty, strong dark ale. The malt may be slightly caramelised to impart toffee notes.
Mild ale
Mild ale originally meant unaged ale, the opposite of old ale. It can be any strength or colour, although most are dark brown. An example of a light-coloured mild is Banks's Original.
Burton Ale
Burton Ale was a strong, dark, somewhat sweet ale brewed to good strength and vatted at the brewery for a year or more. Sometimes used as a 'stock ale' for blending into younger beers, these comparatively strong ales were also enjoyed on their own. Bass No.1 was a classic example of Burton Ale, and in modern times Fullers Golden Pride is often considered by some to be a rare remaining example of a classic Burton style ale. Sometimes Burton ales are considered comparable to Barleywines.
Old Ale
In England, old ale was strong beer traditionally kept for about a year, gaining sharp, acetic flavours as it did so. The term is now applied to medium-strong dark beers, some of which are treated to resemble the traditional old ales. In Australia, the term is used even less discriminately, and is a general name for any dark beer.
Belgian Ales
Belgium produces a wide variety of specialty ales that elude easy classification. Virtually all Trappist beers and Abbey beers are high in alcoholic content but light in body due to the addition of large amounts of sucrose, which provides an alcohol boost with an essentially neutral flavour.
Trappist beers are brewed under direct control of the monks themselves. Of the 171 Trappist monasteries throughout the world, only seven brew beer, of which there are six in Belgium. The seventh is in the Netherlands. Abbey beer is brewed by commercial breweries in the style of a trappist beer, sometimes using the name of a monastery, often one that no longer exists or in some cases one that has licensed its name to a brewery.